5G Core Network Attacks
Attacks targeting the 5G core network functions and interfaces. Explore advanced exploitation techniques targeting virtualized network functions, network slicing, and service-based interfaces.
Understanding Core Network Vulnerabilities
The 5G core network represents a fundamental shift from traditional telecom architectures to cloud-native, service-based designs. This transformation introduces new attack surfaces through virtualization, microservices, and API-driven communications.
Core network attacks target the heart of 5G infrastructure, including critical functions like AMF, SMF, UPF, and NSSF. Successful exploitation can lead to complete network compromise, subscriber data theft, and service disruption across multiple network slices.
Critical Infrastructure
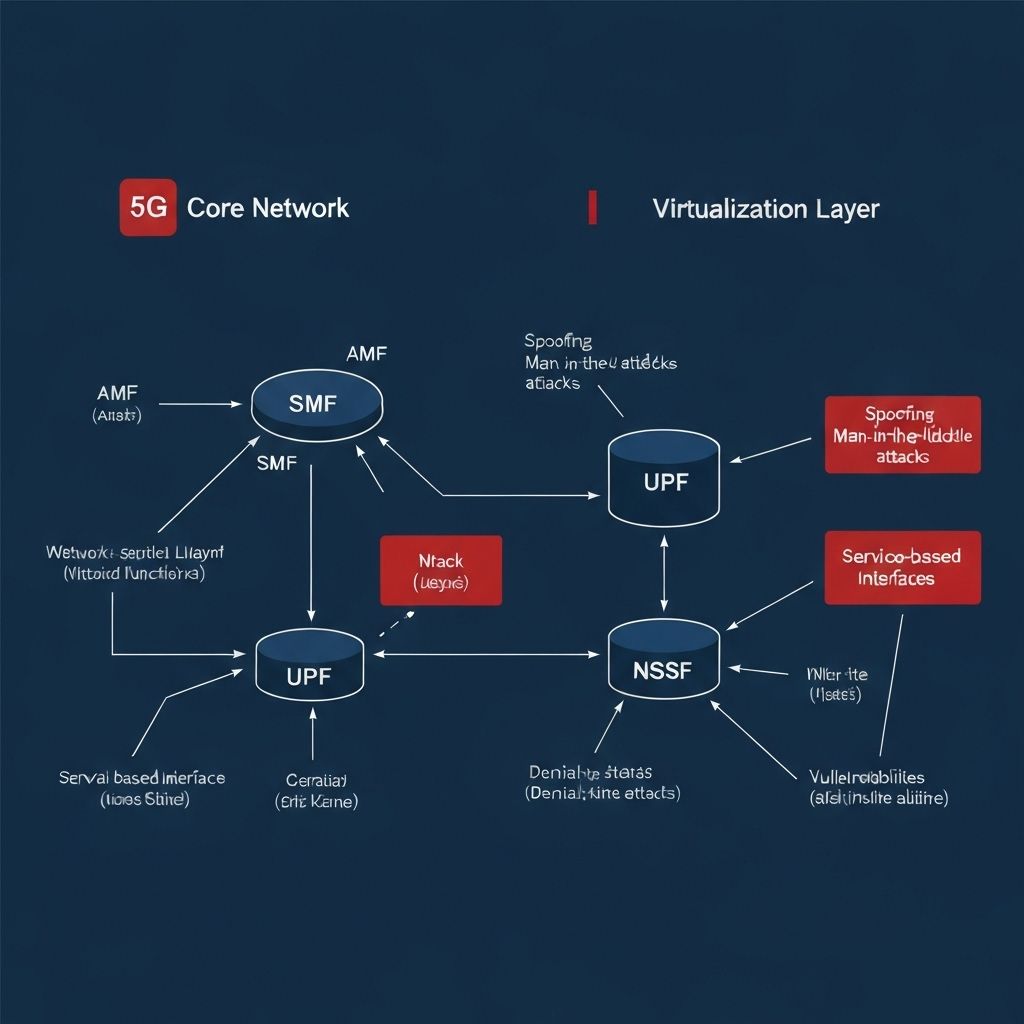
Core Network Attack Vectors
Comprehensive analysis of attack techniques targeting 5G core network infrastructure, virtualization platforms, and service-based interfaces.
Technical Overview
NFV attacks target the virtualized infrastructure that hosts 5G core network functions. These attacks exploit hypervisor vulnerabilities, container escape techniques, and orchestration weaknesses.
Attack Techniques
- Hypervisor escape to gain host access
- Container breakout from isolated VNFs
- VNFM (VNF Manager) exploitation
- Resource exhaustion attacks on shared infrastructure
- Side-channel attacks on co-located VNFs
Primary Targets
Common Tools
Impact
Function compromise, data access, service disruption
Mitigations
Secure NFV platforms, isolation, access controls, regular patching
Technical Overview
Network slicing attacks exploit weaknesses in slice isolation mechanisms to access resources or data from other slices, or to disrupt slice operations through resource manipulation.
Attack Techniques
- Slice isolation breach through shared resources
- Resource exhaustion to impact other slices
- NSSF manipulation for unauthorized slice access
- Cross-slice data leakage exploitation
- QoS parameter manipulation
Primary Targets
Common Tools
Impact
Cross-slice information leakage, resource theft, QoS degradation
Mitigations
Strong slice isolation, resource monitoring, access controls
Technical Overview
Service-based interface attacks target the HTTP/2-based APIs used for communication between 5G core network functions. These attacks exploit authentication weaknesses, injection vulnerabilities, and protocol flaws.
Attack Techniques
- OAuth/JWT token forgery and replay
- API injection attacks (SQL, command, JSON)
- HTTP/2 protocol vulnerabilities
- NRF (NF Repository Function) poisoning
- Man-in-the-middle on SBI communications
Primary Targets
Common Tools
Impact
Unauthorized access to network functions, data manipulation
Mitigations
API security, strong authentication, input validation, TLS
Advanced Exploitation Techniques
Deep dive into sophisticated attack methodologies for compromising 5G core network infrastructure.
Defense Strategies
Comprehensive security measures to protect 5G core network infrastructure from advanced attacks.
• Secure hypervisor configuration and hardening
• Container runtime security and isolation
• Regular patching of virtualization platforms
• Network segmentation between VNFs
• Intrusion detection for VM/container escape
• Strong resource isolation mechanisms
• Dedicated compute/network resources per slice
• NSSF access control and authentication
• Resource usage monitoring and alerting
• Regular slice isolation testing
• Strong authentication (OAuth 2.0, mTLS)
• Input validation and sanitization
• Rate limiting and throttling
• API gateway with security policies
• Regular security audits and penetration testing
• Real-time traffic analysis and anomaly detection
• SIEM integration for security events
• NF behavior monitoring and baselining
• Automated threat response mechanisms
• Security information correlation
• Mutual authentication between all NFs
• Least privilege access controls
• Micro-segmentation of network functions
• Continuous verification and validation
• Encrypted communication channels
• Automated incident detection and alerting
• Predefined response playbooks
• Forensic data collection and analysis
• Rapid containment and remediation
• Post-incident review and improvement
Related Resources
Explore additional resources on 5G security and core network protection.