Radio Interface Attacks
Comprehensive analysis of attack vectors targeting the 5G radio access network (RAN), including rogue base stations, jamming attacks, and subscriber identity interception techniques.
Understanding Radio Interface Attacks
The radio interface, also known as the air interface, is the wireless communication link between user equipment (UE) and the 5G base station (gNodeB). This interface represents a critical attack surface in 5G networks due to its wireless nature and accessibility to potential attackers.
Radio interface attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the 5G New Radio (NR) protocol stack, physical layer security mechanisms, and authentication procedures. These attacks can lead to privacy violations, service disruption, and unauthorized network access.
Wireless Attack Surface
The wireless nature of the radio interface makes it accessible to attackers within physical proximity, requiring no direct network access.
Protocol Vulnerabilities
Despite improvements over 4G, the 5G NR protocol stack still contains exploitable weaknesses in authentication, encryption, and signaling procedures.
Physical Layer Attacks
Attacks targeting the physical layer can disrupt communications through jamming, interference, or signal manipulation techniques.
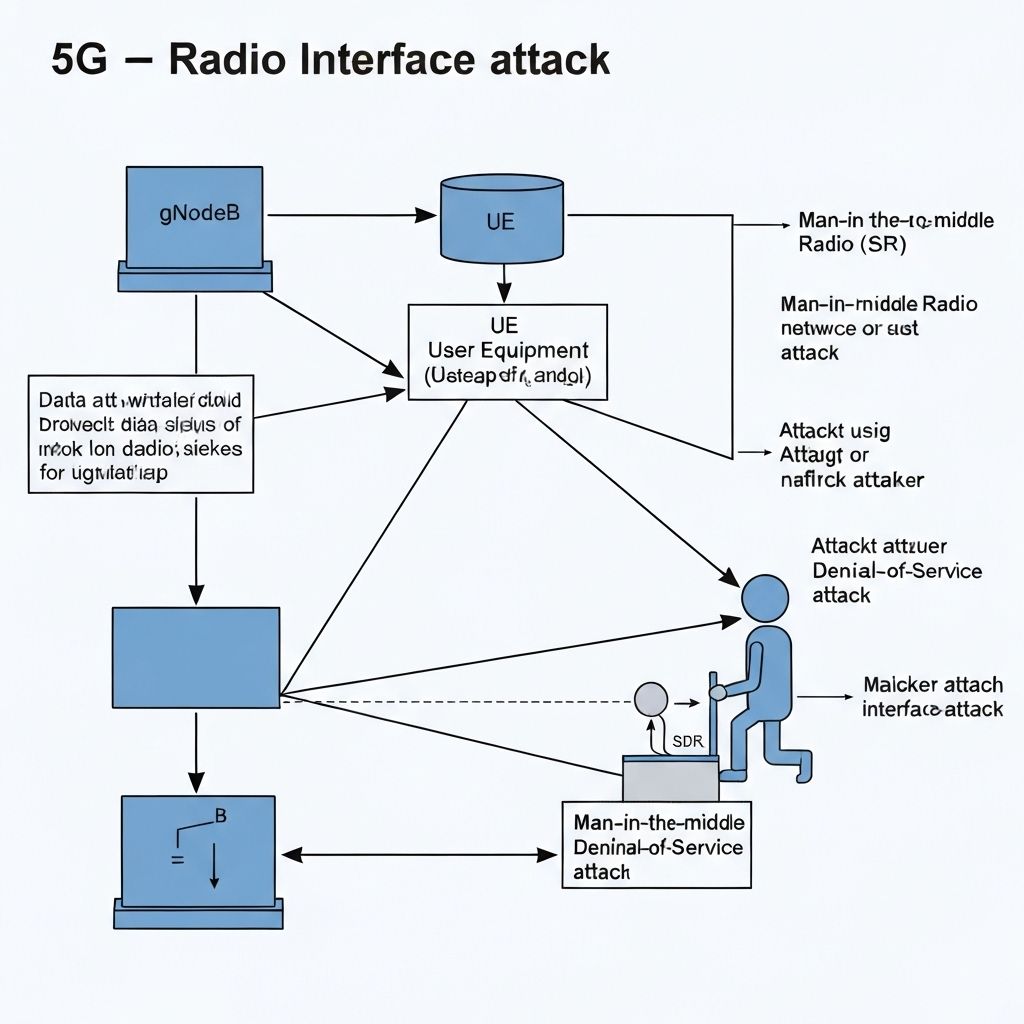
Radio Interface Attack Vectors
Detailed analysis of specific attack vectors targeting the 5G radio access network and air interface.
Technical Deep Dive
A rogue base station (fake gNodeB) attack involves deploying unauthorized radio equipment that mimics a legitimate 5G base station. The attack typically uses Software-Defined Radio (SDR) hardware combined with open-source 5G protocol stacks.
Jamming attacks disrupt 5G radio communications by transmitting interference signals on the same frequencies used by the network. These attacks can target specific channels or the entire frequency band.
5G introduces the Subscription Concealed Identifier (SUCI) to protect the permanent subscriber identity (SUPI) from exposure over the air interface. However, implementation weaknesses and protocol vulnerabilities can still enable identity catching attacks.
Protection Mechanisms
- Public key encryption of SUPI to create SUCI
- Home network decryption of SUCI
- Temporary identifiers (5G-GUTI) for subsequent communications
Potential Weaknesses
- Fallback to unencrypted SUPI in certain scenarios
- Linkability attacks through timing and pattern analysis
- Implementation flaws in SUCI generation
Defense Strategies
Comprehensive mitigation approaches to protect against radio interface attacks in 5G networks.
- Implement strong mutual authentication between UE and gNodeB
- Deploy anomaly detection systems to identify rogue base stations
- Use frequency hopping and beamforming to mitigate jamming
- Implement integrity protection for all signaling messages
- Validate gNodeB certificates and authentication responses
- Implement SUCI encryption correctly without fallback mechanisms
- Monitor for suspicious cell behavior and signal anomalies
- Use secure baseband firmware with regular security updates
- Deploy RF monitoring systems to detect unauthorized transmissions
- Implement machine learning-based anomaly detection
- Monitor for unusual authentication patterns and failures
- Correlate events across multiple network layers
Related Resources
Explore related attack vectors and security topics in 5G networks.